Introduction
In today’s digital era, data is the backbone of every business, regardless of its size or industry. With the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure, the risk of data loss, cyberattacks, and system failures has grown exponentially. Disaster Recovery-as-a-Service (DRaaS) is a crucial solution that helps businesses maintain resilience and ensure continuity in the face of these risks. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about DRaaS, from its basics to its benefits, implementation strategies, and best practices.
Definition
Disaster recovery-as-a-service is a technological backup solution that replicates and recovers data that has been affected by disasters. Disaster recovery-as-a-service is derived from business disaster recovery policies. When catastrophe recovery-as-a-service is implemented properly, business continuity is guaranteed.
What is Disaster Recovery-as-a-Service (DRaaS)?
DRaaS is a cloud-based service that allows businesses to back up and recover critical data and systems in the event of a disaster. Whether it’s a natural disaster, cyberattack, or hardware failure, DRaaS ensures that a company’s operations can be restored quickly and effectively. Unlike traditional disaster recovery, which relies on physical data centers and manual processes, DRaaS leverages the cloud for automation, speed, and flexibility, making it more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Key Components of DRaaS
To fully understand DRaaS, it’s helpful to explore its core components, which include:
Replication: DRaaS providers replicate a business’s data and applications to a secure off-site cloud. This replication process is continuous, ensuring that the data in the cloud is always up-to-date.
Failover: In the event of a system failure or disaster, DRaaS automatically shifts the load to the backup infrastructure in the cloud, allowing business operations to continue with minimal interruption.
Failback: Once the primary systems are back online, DRaaS facilitates the process of switching operations from the cloud back to the original infrastructure.
These components work together to provide seamless recovery, keeping downtime to a minimum and reducing the potential financial impact of a disaster.
How DRaaS Works
DRaaS works by creating a mirror of a company’s IT environment on a cloud platform. This replica is continuously updated to reflect any changes to the production environment, ensuring that the latest data and applications are available in the event of a failure. When a disaster strikes, the DRaaS provider initiates a failover to the cloud infrastructure, allowing employees to access applications and data as if nothing has happened.
The DRaaS provider then helps facilitate the failback process when the primary systems are restored, syncing any changes made during the downtime to maintain data integrity. DRaaS is typically billed as a subscription service, with pricing based on factors such as data storage, the number of users, and specific recovery requirements.
The Benefits of DRaaS
The rise of DRaaS has brought about numerous benefits that traditional disaster recovery methods often lack. Some of the main benefits include:
Cost Savings: By leveraging the cloud, DRaaS eliminates the need for costly secondary data centers and extensive hardware investments. Businesses pay only for the resources they use, making it an affordable option even for small businesses.
Scalability: DRaaS is highly scalable, allowing businesses to increase or decrease their recovery capabilities as needed without investing in additional infrastructure.
Speed and Efficiency: DRaaS automates the failover and failback processes, minimizing downtime and ensuring that data and applications are accessible as quickly as possible.
Improved Security: Leading DRaaS providers use advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with industry standards to ensure that data remains secure.
Simplified Management: With DRaaS, IT teams have fewer infrastructure demands and can rely on the provider for monitoring, updates, and maintenance, allowing them to focus on core business tasks.
Types of DRaaS Solutions
Businesses can choose from different types of DRaaS solutions, each suited to various needs and budgets:
Self-Service DRaaS: In this model, the business is responsible for managing and implementing the disaster recovery processes. The DRaaS provider only supplies the infrastructure and tools.
Managed DRaaS: The provider takes full responsibility for disaster recovery, including failover, failback, and ongoing monitoring. This option is suitable for businesses with limited IT resources.
Assisted DRaaS: This hybrid approach allows the business to work closely with the DRaaS provider, sharing responsibilities. The provider may handle failover and failback while the business manages data replication.
Choosing the Right DRaaS Provider
Selecting a DRaaS provider is a critical decision that requires careful evaluation of the business’s needs and the provider’s capabilities. When assessing DRaaS providers, consider the following factors:
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO): Ensure that the provider can meet your desired RTO (how quickly you need systems back online) and RPO (how much data you can afford to lose).
Data Center Location: Choose a provider with data centers in locations that are safe from natural disasters common in your area.
Compliance and Security: Ensure the provider complies with relevant industry standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and uses robust security measures.
24/7 Support: In a disaster scenario, around-the-clock support is essential to ensure issues are resolved quickly.
Testing Capabilities: Regular testing is crucial for effective disaster recovery. Ensure the provider allows periodic testing to validate the recovery plan.
Cost Structure: Understand the provider’s cost structure and ensure it aligns with your budget and needs.
Implementing DRaaS: Best Practices
Once you’ve chosen a DRaaS provider, follow these best practices to ensure a smooth implementation:
Conduct a Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks to your business’s data and IT infrastructure. This will assist you in modifying the DRaaS solution to target your unique weaknesses.
Define RTO and RPO: Determine the acceptable downtime (RTO) and data loss (RPO) to ensure that your DRaaS solution aligns with your recovery requirements.
Establish Clear Communication Channels: Involve all stakeholders, including IT teams, management, and the DRaaS provider, to define roles and responsibilities.
Regularly Test the DRaaS Solution: Conduct regular testing to identify any weaknesses in the recovery process and make necessary adjustments. Testing should mimic real disaster scenarios to ensure effectiveness.
Monitor and Update the DR Plan: As your business grows and changes, your disaster recovery plan should evolve as well. Regularly review and update the plan to keep it relevant.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While DRaaS offers many advantages, there are some challenges that businesses may encounter:
Data Transfer Latency: Transferring large volumes of data to the cloud can lead to latency issues. Work with your provider to optimize data transfer methods and consider solutions like edge computing to reduce latency.
Compliance Concerns: Some industries, like healthcare and finance, have strict regulatory requirements for data storage and recovery. Choose a DRaaS provider that has experience with your industry’s compliance standards.
Cost Control: While DRaaS can be cost-effective, costs can rise if not managed carefully. Monitor usage and negotiate transparent billing structures with your provider.
The Future of DRaaS
As technology continues to evolve, DRaaS will become even more advanced and integral to business continuity strategies. Innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are set to play a significant role, with AI-driven analytics helping businesses predict potential disruptions and automate recovery processes more effectively. Furthermore, as edge computing and 5G networks gain traction, DRaaS will likely become faster and more accessible, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
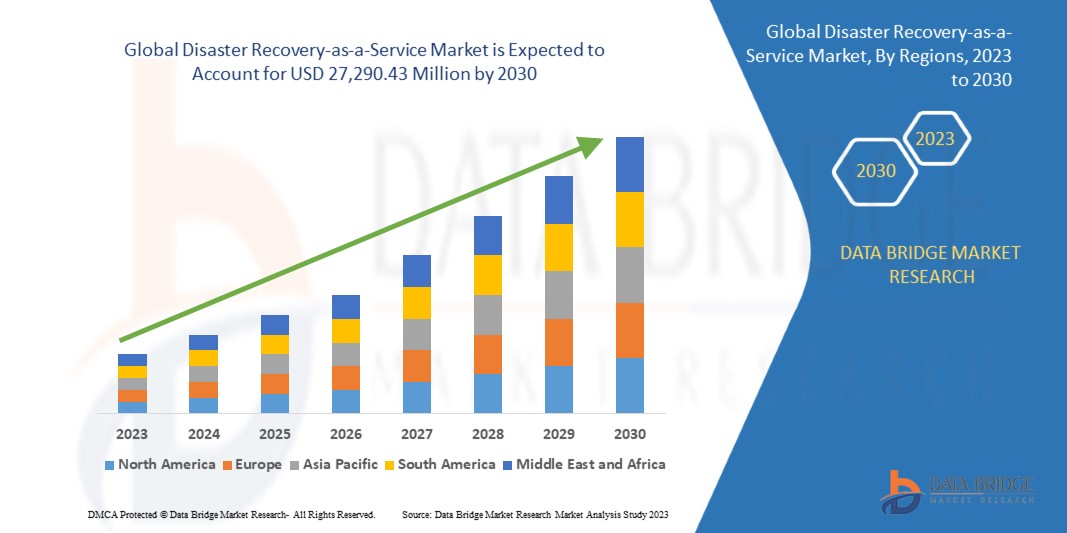
Growth Rate of Disaster Recovery-as-a-Service Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the disaster recovery-as-a-service market, which was valued at USD 11,652.35 million in 2022, is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.9% to reach USD 27,290.43 million by 2030.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-disaster-recovery-service-market
Conclusion
In an unpredictable digital landscape, DRaaS is a powerful solution for safeguarding business operations, data, and reputation. By choosing the right DRaaS provider, implementing best practices, and staying vigilant about testing and updates, businesses can effectively prepare for unexpected disasters and minimize downtime. In the end, DRaaS is not just an investment in data protection but a commitment to resilience and customer trust. Embracing DRaaS is essential for any business looking to maintain continuity and thrive amid digital uncertainty.